How to calculate the ROI of ERP?
Learn how to measure the return on investment on ERP systems (ROI) by comparing various costs against the financial and operational benefits gained.

Quick summary
The article explains how to calculate the ROI of an ERP system by comparing total benefits to total costs by outlining the key cost and benefit components, both tangible and intangible. We have included a simple five-step process and formula to help guide accurate calculations.
Learn more about our solutions
ROI explained
A mid and back-office solution, also known as an ERP solution (Enterprise Resource Planning) system, plays an important role in modern businesses by streamlining operations, improving efficiency and driving growth. However, ERP implementations require significant investment, making it vital to evaluate the return on investment (ROI). Understanding the ROI of an ERP implementation ensures you can justify the cost and make informed decisions about the system’s value to your organization. This article breaks down the process of calculating the ROI of ERP in simple terms to help you make the most of your investment.
What is ROI and why it matters for ERP?
ROI, or return on investment, is a metric used to evaluate the financial benefits of an investment compared to its costs. In the context of ERP systems, ROI measures how much value the system brings to your organization relative to what you’ve spent.
You can also use this to calculate the back payment timeframe. Here, “the lower the better” is the rule.
Understanding the ROI of ERP is essential because it:
- Justify the investment: Calculating the value of the investment helps stakeholders understand the system’s value.
- Supports decision-making: : Understanding the ROI guides future investments and upgrades.
- Tracks success: The ROI is a benchmark to help you measure the ERP system’s impact on business performance.
By calculating the ROI of your ERP investment, businesses can identify whether the system meets expectations and aligns with long-term goals.
Payback ratio
If you divide your net benefit by your current cost (current cost – any cost reductions), you will see the back payment ratio. The lower the better.
Components of ERP ROI calculation
To calculate ERP ROI, you need to consider both costs and benefits.
If you are calculating a back payment ratio, you should also consider any cost reductions (hosting vs. internal servers, backup, etc.)
Costs:
(A) Upfront costs:
o Software licenses or subscriptions.
o Hardware for on-premises systems or cloud infrastructure.
o Implementation costs, including consultants and deployment.
(B) Ongoing costs:
o Maintenance and support fees.
o Training costs for staff.
o Periodic updates or upgrades.
Benefits:
(A) Tangible benefits:
o Savings on labor costs due to automation and customer self-service. o Increased revenue from improved customer experience.
o Ability to provide additional products and services not possible in the legacy system.
(B) Intangible benefits:
o Improved decision-making with real-time data insights.
o Enhanced collaboration across departments.
o Scalability to support future business growth. o Lack of the traditional update cost due to evergreen (always the latest version)
The formula to calculate the ROI of ERP
The standard formula for ROI is:
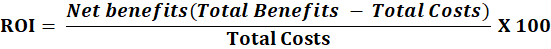
This formula gives a percentage representing the return on your investment. A positive ROI indicates that the benefits outweigh the costs, while a negative ROI suggests the need for adjustments to your ERP strategy.
Steps to Calculate the ROI of ERP
Let’s break the calculation into five easy steps:
Step 1: Identify all costs
Start by listing all upfront and ongoing costs associated with your (NEW) ERP system. This includes software, hardware, implementation, and maintenance expenses. Be thorough to avoid underestimating costs.
Step 2: Measure tangible benefits
Quantify direct benefits, such as:
- Reduced operational costs through automation.
- Increased sales revenue due to improved customer service.
Step 3: Estimate intangible benefits
Although harder to quantify, intangible benefits add significant value. For example:
- Time saved on manual processes.
- Better decision-making through real-time analytics.
- Employee satisfaction from streamlined workflows.
Step 4: Calculate net benefits
Subtract the total costs from the total benefits to determine the net benefits.
Step 5: Apply the formula
Using the ROI formula, divide the net benefits by total costs and multiply by 100.
Proven techniques for accurate ROI measurement
Here are some effective techniques to ensure accurate ROI calculations:
1. Use case studies: Analyze the ROI achieved by businesses similar to yours. For instance, a travel business might find insights from case studies in the same industry.
2. Use analytics tools: Most ERP systems offer analytics features that track key performance indicators (KPIs) like operational efficiency and cost savings.
3. Conduct regular reviews: Monitor your ERP system’s performance periodically to ensure it continues to deliver value and adapt strategies as needed.
Real-world examples of ERP ROI in travel agency
62oN, a travel agency using A dedicated travel management and ERP solution, optimized its booking processes by increasing the speed and efficiency that they were lacking earlier, with a bonus of flexibility in their system.
These examples demonstrate the significant impact of ERP systems on business performance when ROI is carefully calculated and monitored.
Want to know the full value of your ERP system?
Want to know more about data utilisation
See our latest insight
-

Why most travel agencies are not ready to succeed with AI
AI promises more than most travel agencies will be able to realize today.
-

Customer story: Wings Global Travel
Building global scalability with TravelOperations and Microsoft Dynamics 365
-

What’s next for travel? Travel industry insights 2025
Discover the top travel industry trends for 2025 & 2026: From solo travel to smart tech and sustainability.